Safe shopping guarantee. You will receive your product or your money back. See details
Dietary supplement
Beauty Hair™
Comprehensive support for hair, skin, and nails
As many as 13 active ingredients!
Keratin Cynatine®, L-cysteine, L-methionine, L-lysine, bamboo shoot extract, sabal palm extract, celery seed extract, B3, B5, B6, biotin, my-inositol, zinc
French keratin Cynatine® clinically proven to deliver a positive effect on hair condition
Highly standardised botanical extracts
Tested microbiologically, for heavy metals, alkaloids, pesticides and ethylene oxide
Quantity: 60 capsules / 30 daily servings
Best before: 08.2027
Notified to GIS (Poland): BZ/SD/POW/PL1000D/001450/2025, w BLOZ: 3024689
Encapsulated and manufactured in Poland
257 in stock
Price per piece: 2,5 zł


Previous lowest price was 149,99 zł.
Comprehensive support for hair, skin, and nails. Keratin Cynatine®, L-cysteine, L-methionine, bamboo shoot extract, sabal palm extract, celery seed extract, B3, B5, B6, biotin, my-inositol, PABA, zinc.
Dietary supplement
Beauty Hair™
Comprehensive support for hair, skin, and nails
As many as 13 active ingredients!
Keratin Cynatine®, L-cysteine, L-methionine, L-lysine, bamboo shoot extract, sabal palm extract, celery seed extract, B3, B5, B6, biotin, my-inositol, zinc
French keratin Cynatine® clinically proven to deliver a positive effect on hair condition
Highly standardised botanical extracts
Tested microbiologically, for heavy metals, alkaloids, pesticides and ethylene oxide
Quantity: 60 capsules / 30 daily servings
Best before: 08.2027
Notified to GIS (Poland): BZ/SD/POW/PL1000D/001450/2025, w BLOZ: 3024689
Encapsulated and manufactured in Poland
257 in stock
Previous lowest price was 149,99 zł.
Price per piece: 2,5 zł


Safe shopping guarantee. You will receive your product or your money back. See details
BEAUTY HAIR™ dietary supplement is a formula provided in capsules containing keratin hydrolysate Cynatine® HNS, L-cysteine, L-methionine, L-lysine, bamboo shoot extract DER 98:1 standardised to contain 70% silica, saw palmetto fruit extract DER 20:1 standardised to contain 45% fatty acids, celery seed extract DER 98:1 standardised to contain 98% apigenin, vitamin B3, vitamin B5 as calcium D- pantothenate, vitamin B6 as p-5-p, biotin as D-biotin, inositol as myo-inositol, zinc as zinc gluconate.
Cynatine® HNS solubilised keratin:
- significantly reduces hair loss
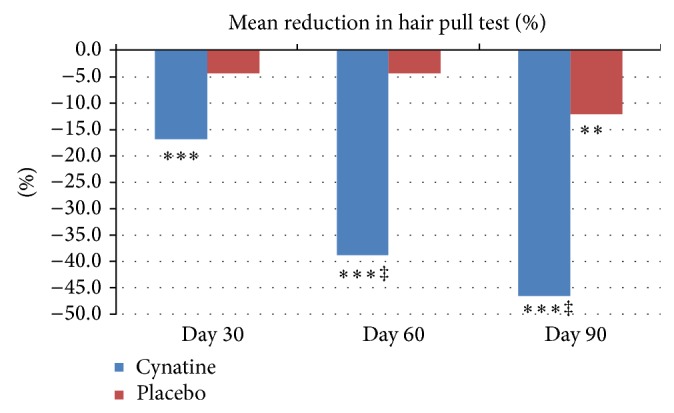
(the study showed a 12.5% reduction in hair loss when compared to placebo at day 30 and a 34.5% and 34.4% reduction at days 60 and 90, respectively), - improves the anagen and telogen phases
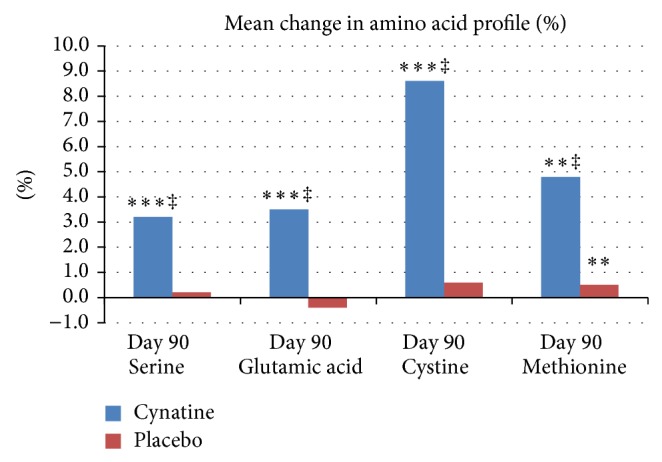
(by 9.2% when compared to placebo at day 90 of the test period), - increases the content of 4 amino acids particularly important for hair
(serine, glutamic acid, cystine and methionine) – measured based on their ratio to the total hair protein content, - boosts hair tensile strength,
- improves the overall appearance of hair
(effects assessed subjectively by study participants, the percentage improvement when compared to placebo was 17.6% at day 30, 35.3% at day 60 and 47.1% at day 90), - reduces nail tendency to break,
(87.5% of subjects taking Cynatine® HNS showed improvements in this area), - promotes nail firmness
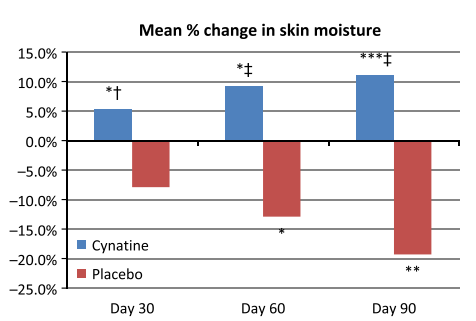
(at baseline 37.5% of subjects had hard nails and at day 90 87.5% had hard nails), - promotes water retention through the skin
(almost 80% of subjects on Cynatine® HNS treatment showed improvement in skin hydration), - improves skin elasticity
(87.5% of subjects on the Cynatine® HNS treatment showed improved skin elasticity at day 90), - reduces the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles
(results measured using three methods showed an 11.5% reduction in wrinkles in subjects on Cynatine® HNS at day 90), - increases the protein content of the skin improving its cohesivity and preventing flabbiness
(19.7% improvement in skin protein content at day 90 when compared to the placebo group; 95.8% of the subjects using Cynatine® HNS showed improvements in skin cohesivity), - improves the appearance of skin and wrinkles
(58.3% of the subjects using Cynatine® HNS showed improvements in dermatological assessment of skin wrinkles at day 90; subjects on placebo showed no clinical improvement).
These conclusions are based on two studies conducted with 500 mg Cynatine® HNS treatment/day (the amount contained in the daily portion of BEAUTY HAIR™). To find the references to the graphs showing the effects and the two published studies, go to the module below and click on Keratin – why did we choose French Cynatine® HNS?
L-Cysteine:
- helps maintain healthy hair and nails,
- helps stabilise the protein structure,
- supports colagen formation,
- is a source of sulphur.
L-Methionine
- helps maintain healthy hair and nails,
- helps stabilise the protein structure,
- supports colagen formation,
- improves hair and nails health,
- supports lipid metabolism.
Silicon:
- is essential for normal bone and connective tissue formation,
- supports the maintenance of healthy connective tissue in the skin by stimulating collagen synthesis in the dermis,
- helps support good hair quality,
- strengthens joint cartilage and intervertebral discs.
Saw palmetto:
- is a source of fatty acids, phytosterols such as beta-sitosterol, beta-carotene, vitamin E derivatives and polysaccharides,
- lowers dihydrotestosterone (DHT) by inhibiting the activity of 5α-reductase; excess DHT has a detrimental effect on hair follicles and is responsible for their miniaturisation and consequently weaker and falling hair; high DHT levels are also responsible for skin hyper seborrhoea.
Apigenin:
- is a flavanoid, an organic compound present in plants, which exhibits antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties,
- by reducing TGF-beta1 expression, it allows the anagen phase to continue, stopping hair loss,
- stimulates the elongation of hair follicles, a process necessary for the anagen phase of hair growth.
| Ingredient | Amount per daily serving 2 capsules |
|
| Cynatine® HNS keratin hydrolyzate | 500 mg | – |
| L-cysteine | 200 mg | – |
| L-methionine | 170 mg | – |
| L-Lysine Hydrochloride | 140 mg | – |
| Bamboo shoot extract (Bambusa vulgaris Schrad.) DER 20:1, standardized to 70% silica |
100 mg | – |
| Saw palmetto fruit extract (Serenoa repens) DER 20:1 standardized to 45% fatty acids | 70 mg | – |
| Celery seed extract (Apium graveolens) DER 98:1 standardized to 98% apigenin | 5,72 mg | – |
| Vitamin B3 (nicotinamide) | 10 mg | 62,5% DV* |
| Vitamin B5 (calcium D-pantothenate) | 10 mg | 166,7%DV* |
| Vitamin B6 (pyridoxal 5′-phosphate) | 6 mg | 428,6%DV* |
| Biotin (D-Biotin) | 2500 mcg | 5000%DV* |
| Inositol (myo-inositol) | 80 mg | – |
| Zinc (zinc gluconate) | 10 mg | 100%DV* |
| Acacia Fiber | 13,3 mg | – |
| L-Leucine | 42 mg | – |
*DV – Daily Value
Ingredients: Cynatine® HNS keratin hydrolyzate, L-cysteine, L-methionine, L-Lysine Hydrochloride, hydroxypropyl methylcellulose – Vcaps®PLUS vegetable capsule, bamboo shoot extract, saw palmetto fruit extract, acacia fiber, zinc gluconate, myo-inositol, L-leucine, pyridoxal 5 ‘-phosphate, p-aminobenzoic acid, calcium D-pantothenate, nicotinamide, celery extract, D-biotin.
Gluten-free.
Servings per container: 30.
Take 2 capsules daily.
Do not exceed suggested use. Dietary supplements should not replace a varied diet. The product is recommended for adults. Suitable for vegans.
Warning: if pregnant or nursing, consult your doctor before use.
Capsule size: “00” (22 mm in length).
Organoleptic properties: white powder with a bitter-salt taste, poorly soluble in water.
Keep away from the sun at a temperature below 25°C in the original packaging, out of reach of small children.
Production lot number / Best before – see the unit label (left side of the label).
Batch tests performed towards:
- Microbiology: the presence of listeria, staphylococcus, Escherichia coli and coli groups, salmonella, total microbial count,
- heavy metals (arsenic, cadmium, lead, mercury),
- ethylene oxide and 2-chloroethanol,
- gluten content.
The tests were carried out at the independent, accredited Laboratorium GBA Polska – Certificates of Accreditation no: AB 1095.



Comprehensive support for hair, skin, and nails
Keratin is one of a highly heterogeneous family of fibrillar proteins of a compact structure with a high cysteine content.
The hair fibre is made up of three basic morphological components: the cuticle (keratin scales), the cortex and the medulla.
From an aesthetic point of view, the beauty and health of hair depend on the condition of the hair cuticle. Most hair cosmetic products and hair treatments initially affect the cuticle, changing the appearance, softness and even texture of the hair. As the main component of the hair cortex, keratin contributes to strengthening the hair. It is important in restoring or improving the mechanical strength of damaged hair fibres.
Keratin proteins are hard, insoluble compounds that are hard to absorb. Solubilised keratin, i.e. with increased solubility, is highly bioavailable. Keratin is also characterised by its resistance to proteolytic enzymes such as trypsin, pepsin and papain. This means that it is not digested like other proteins.
The effect of bioavailable, patented, solubilised keratin Cynatine® HNS was proved by:
- hair loss reduction (up to 34.5% when compared to placebo at day 60), hair strength and shininess improvement
Mean percentage reduction in the hair pull test compared to baseline for placebo and Cynatine® HNS. (1)
- anagen and telogen phases improvement (by 9.2 % when compared to the placebo group at day 90 of the test period)
What does this mean?- Anagen is the first phase of the hair cycle involving the proliferation of hair follicle cells, i.e. stimulation of hair growth. Cynatine® HNS stimulates the growth of hair follicles, which causes faster hair growth/re-growth.
- Telogen is the rest phase. A prolonged rest phase is key in preventing, for example, alopecia areata.
- the effect on an increase of all 4 amino acids essential for hair based on their ratio to total protein content,
Mean percentage change in amino acid profile from baseline for placebo and Cynatine® HNS. (1)
- protection against water loss through the skin (subjects in the placebo group showed significant deterioration in skin hydration as a result of the prevailing weather conditions – the study was conducted in winter),
Mean percentage change in skin hydration for placebo and Cynatine® HNS. (2)
- reduction in and smoothing of fine lines and wrinkles,
- support in the maintenance of skin firmness and elasticity,
Mean percentage change in skin elasticity for placebo and Cynatine® HNS. (2)
- reduction in skin redness caused by inflammation,
- fine skin tone and brightness,
- improved nail strength, flexibility and enhanced moisturisation of the nail plate.
Keratin promotes an improved skin appearance thanks to its natural antioxidant properties related to its effect on the production of superoxide dismutases and glutathione (GSH).
These conclusions are based on randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trials published in two journals (International Journal of Cosmetic Science, and the Scientific World Journal). In both studies, the active group received 500 mg of Cynatine® HNS plus zinc, copper, and vitamins B3, B5, B6, and B7 for 90 days. The same ingredient in the same amount is contained in BEAUTY HAIR™.
The results show that subjects on Cynatine® HNS showed a statistically significant improvement in hair and nail condition when compared to placebo, making Cynatine® HNS an effective product for improving hair and nail condition in 90 days or less.
BEAUTY HAIR™ contains the following vitamins:
- Vitamin B3 / PP (nicotinamide)
- Vitamin B5 (calcium D-pantothenate)
- Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxal5′-Phosphate, P 5′-P)
- D-Biotin, Vitamin B7 / HH
- Inositol (myo-inositol), though referred to as Vitamin B8, it is not actually a vitamin
- PABA, para-aminobenzoic acid, commonly referred to as Vitamin B10.
What supporting effect do these vitamins have on hair, skin and nails?
Niacin (vitamin B3) supports healthy skin, which is necessary for keeping hair in the proper state.
Pantothenic acid (vitamin B5) prevents too early hair greying.
Vitamin B6, pyridoxine, is involved in protein metabolism. As a cofactor, it activates enzymes and enables the chemical reactions that start the metabolism of the hair proteins, keratin and melanin in the hair follicles. Together with cysteine, it helps prevent hair loss.
Vitamin B6 also controls the release of hormones. The active form of pyridoxal 5-phosphate regulates the androgens: testosterone and oestrogen. These hormones have a direct effect on hair growth. Dihydrotestosterone, a metabolite of testosterone, negatively affects hair growth and leads to hair loss by shortening the length of the anagen phase and reducing the size of hair follicles. According to studies, vitamin B6 binds to testosterone receptors and stops the formation of DHT.
Biotin (vitamin B7) is a vitamin taking part in fat and protein metabolism and its deficiency might lead to hair loss. Thanks to the presence of Sulphur in the biotin structure, it influences the state of skin integument lowering sebum secretion and activating hair growth
Para-aminobenzoic acid (PABA) is functionally linked to hair quality, particularly melanogenesis. Hair melanogenesis is tightly linked to the stages of the hair cycle and is actively pigmented during anagen (growth) but not in catagen or telogen. One study investigated the effect of PABA at 12–24 g/day on age-related grey hair. 35% of the patients noted hair darkening after 2–10 months of treatment.
In randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trials published in two journals (International Journal of Cosmetic Science, the Scientific World Journal), from which the conclusions drawn in the question above were drawn, the active groups received vitamins B3, B5, B6, B7 in addition to Cynatine® HNS.
DHT is the active form of testosterone. The enzyme 5α-reductase catalyzes the conversion of testosterone to highly active androgen dihydrotestosterone (DHT). Elevated levels of this hormone, by miniaturisation of hair follicles, lead to androgenetic alopecia, and excessive seborrhoea in the scalp.
Saw palmetto, a botanical extract with anti-androgenic properties, has gained popularity for its benefits on hair regrowth after androgenetic and telogenetic alopecia and improvement in seborrhoeic dermatitis.
The extract is primarily comprised of fatty acids, phytosterols such as beta-sitosterol (0.1%), β-carotene, vitamin E derivatives and polysaccharides.
Saw palmetto supports the reduction of DHT by inhibiting the activity of 5α-reductase, the enzyme that converts testosterone into dihydrotestosterone (DHT).
Beta-sitosterol, one of the components of saw palmetto, is a competitive, non-selective inhibitor of both isoforms (types1 and 2) of 5α-reductase, blocking the nuclear uptake of dihydrotestosterone (DHT) and decreasing DHT binding capacity to androgen receptors by nearly 50%.
Saw palmetto fatty acid components directly inhibit 5α-reductase enzyme activity, aid in the enzyme’s selective hormone transformation processes, and influence access to cofactors by affecting the enzyme’s conformational (spatial structure) state.
Many bioactive compounds present in plants show functional activity. The largest group of naturally-occurring polyphenols are the flavonoids, including apigenin.
Apigenin is a promising ingredient in supplements dedicated to hair loss prevention and hair growth stimulation. Androgen-inducible transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta1), present in the dermal papilla cells, signals the hair follicles to complete the anagen growth phase and enter the catagen transition phase. By decreasing TGF-beta1 expression, apigenin enables the continuation of the anagen phase.
In chemical terms, silica is silicon dioxide (SiO2).
Silicon is an essential trace element involved in the metabolism of connective tissue. It plays an important role by activating hydroxylation enzymes to synthesize collagen, improving its elasticity and strength.
Physiological concentrations of orthosilicic acid (OSA) stimulate fibroblasts to secrete collagen type I. Collagen and the fibres it forms are responsible for the biomechanical properties of the skin. They present as essential components of the structural integrity of the connective tissue and are present in large quantities in the skin, bones and joints. A reduction in the amount of collagen in the skin of about 1% per year after 21 years of age is described, resulting in thickness reduction and elasticity loss, which is directly related to the wrinkles depth.
The right structure and amount of collagen ultimately translate into better skin, hair and nails. Higher silicon content in the hair means a lower falling rate and increased elasticity and smoothness shown in healthier-looking, shiny hair.
There are two amino acids in BEAUTY HAIR™: L-cysteine and L-methionine.
L-cysteine is an essential sulphur-containing amino acid that is involved in many metabolic pathways. It is a key component of the keratin protein due to its ability to form disulphide bridges, which provide strength and rigidity to keratin.
L-Cysteine promotes a significant up-regulation of keratin expression as a result of de novo protein synthesis, while the lack of iron impairs keratin expression. Cysteine supplementation counteracts the adverse effects of iron deficiency on cellular keratin expression, probably by increasing the metabolic availability of iron for DNA synthesis.
Cysteine, as a keratin ingredient, occurs in hair in the highest amount (10-17%) and is one of the endogenous amino acids whose synthesis is dependent on methionine presence. Growth rate, hair diameter and protein synthesis depend on cysteine. The active form of vitamin B6 (pyridoxal 5-phosphate) increases L-cysteine incorporation into keratin.
L-methionine is a sulphur-containing essential amino acid and a precursor of succinyl-CoA, homocysteine, cysteine, creatine and carnitine. Maintaining healthy hair is possible by promoting anagen, delaying catagen and ultimately preventing or reversing hair loss. Nutritional deficiencies have also been linked to hair loss. Hair growth and quality are dependent on dietary protein, including the intake of methionine, an exogenous amino acid.
Methionine is a powerful antioxidant, as is cysteine. An L-methionine- and L-cysteine-enriched diet, in addition to having a significant effect on the structure of the skin and hair, can be beneficial during ageing to protect cells, including neurons, from oxidative imbalance and mitochondrial dysfunction, thus preventing the progression of neurodegenerative processes.
Zinc is an essential trace element. Its main dietary sources are fish and meat. Zinc deficiency can be caused by consuming large amounts of cereal grains (which contain phytate, considered to be a zinc chelating agent), in people who eat small amounts of meat and in infants fed with modified milk. Other causes of zinc deficiency include anorexia nervosa, intestinal disease and cystic fibrosis. Excessive alcohol consumption, cancer, burns, infections and pregnancy can result in increased metabolism and excretion of zinc and therefore an increased need for this micronutrient.
Hair loss is a recognisable sign of zinc deficiency, with hair regrowth following zinc supplementation. Zinc supplementation is recommended if zinc levels are < 70 µg/dl. Numerous studies have shown low zinc levels in subjects affected by hair loss compared to control groups and a strong correlation between zinc deficiency (<70 µgdl) and hair loss.